The Baltic countries, Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania, stand as beacons of resilience and progress on the shores of the Baltic Sea. Their shared history, unique cultural traditions, and burgeoning economic cooperation have shaped a region that is both captivating and inspiring.
From the medieval grandeur of Tallinn to the vibrant streets of Riga, the Baltic countries offer a rich tapestry of experiences. Their shared struggles for independence and their deep-rooted cultural heritage have forged a strong sense of unity among these nations.
Baltic Region Overview
The Baltic region encompasses the countries of Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania, located on the eastern shores of the Baltic Sea. Historically, the region has been a crossroads of trade and cultural exchange, influenced by both Western and Eastern European powers.
Geographical Location
The Baltic region is situated in Northern Europe, bordered by the Baltic Sea to the west, Russia to the east, and Poland and Belarus to the south. The region’s coastline is dotted with numerous islands and peninsulas, creating a diverse and picturesque landscape.
The Baltic countries, with their rich history and stunning landscapes, offer a captivating travel experience. For a unique wildlife encounter, consider a visit to Belfast Zoo , home to a diverse range of animals from around the world. After exploring the zoo’s exhibits, return to the Baltic countries to continue your exploration of this captivating region.
Historical Context
The Baltic region has a rich and complex history, dating back to the Viking Age. Over the centuries, the region has been ruled by various powers, including the Teutonic Knights, the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, the Russian Empire, and the Soviet Union. After regaining independence in 1991, the Baltic countries have emerged as vibrant and prosperous democracies, integrated into the European Union and NATO.
The Baltic countries, Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania, boast a rich cultural heritage and stunning landscapes. If you find yourself in the region, be sure to visit the 230 fifth rooftop bar in Vilnius, Lithuania. This chic rooftop bar offers breathtaking panoramic views of the city and serves a delectable menu of cocktails and cuisine.
After enjoying the nightlife in Vilnius, continue your exploration of the captivating Baltic countries, where you’ll discover a blend of history, nature, and modern charm.
Baltic Countries
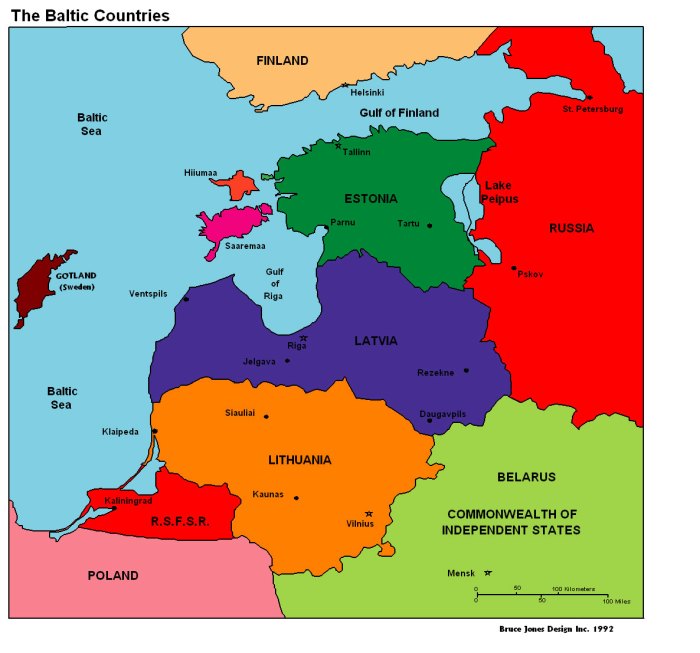
The Baltic region, located in Northern Europe, comprises three countries: Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania. These nations share historical, cultural, and linguistic similarities, and have a combined population of approximately 6 million people.
Political Systems
All three Baltic countries are parliamentary republics, with democratically elected parliaments and presidents. The parliaments hold legislative power, while the presidents serve as heads of state and represent their respective countries abroad.
Economic Development
Since regaining independence in the early 1990s, the Baltic countries have experienced significant economic growth and development. They have transitioned from centrally planned economies to market economies, and have become members of the European Union and NATO.
- Estonia: Estonia is the most economically developed of the Baltic countries, with a GDP per capita of over $25,000. It has a strong IT sector and is known for its e-governance initiatives.
- Latvia: Latvia’s economy is based on agriculture, manufacturing, and tourism. It has a GDP per capita of approximately $18,000.
- Lithuania: Lithuania has a diversified economy with a strong focus on manufacturing, agriculture, and services. Its GDP per capita is around $20,000.
Cultural Heritage
The Baltic countries, Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania, share a rich and diverse cultural heritage that has been shaped by centuries of history and geography. Despite their relatively small size, these countries boast a unique blend of traditions, folklore, and art that reflects their shared experiences and influences.
The Baltic countries have a long history of being influenced by both Eastern and Western cultures. This is reflected in their language, religion, and architecture. For example, Estonian is a Finno-Ugric language, while Latvian and Lithuanian are Indo-European languages. The majority of the population in Estonia and Latvia is Lutheran, while Lithuania is predominantly Catholic.
Folklore, Baltic countries
The Baltic countries have a rich tradition of folklore. This includes folk tales, legends, and myths. Many of these stories are based on the natural world and the people’s relationship with it. For example, the Estonian epic poem “Kalevipoeg” tells the story of a giant who helps to create the Estonian landscape.
The Baltic countries of Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania share a rich history and culture. However, when it comes to timekeeping, they follow the Berlin time , which is one hour ahead of their geographical time zone. This alignment is due to historical and economic factors, as the Baltic countries have close ties with Germany.
Despite the time difference, the Baltic countries maintain their unique identities and continue to embrace their own traditions and customs.
Art
The Baltic countries have a strong tradition of art. This includes painting, sculpture, and architecture. Many of the artists from these countries have been influenced by both Western and Eastern traditions. For example, the Estonian painter Johann Köler was influenced by the Dutch Golden Age painters. The Latvian sculptor Kārlis Zāle was influenced by the French sculptor Auguste Rodin.
Economic Cooperation
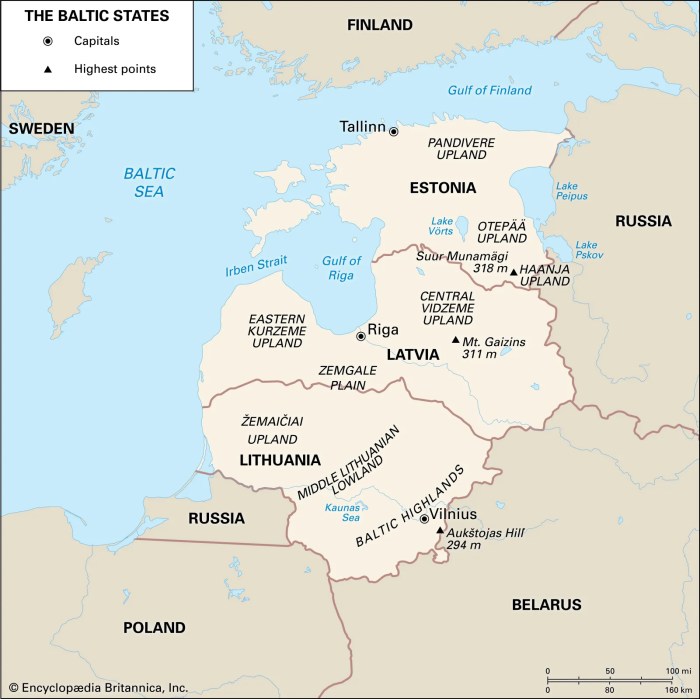
The Baltic countries, Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania, share strong economic ties, fostered by their geographic proximity and historical connections. They actively participate in regional organizations and have benefited significantly from their membership in the European Union.
Participation in Regional Organizations
The Baltic countries are members of the Council of the Baltic Sea States (CBSS), a regional forum for cooperation among the countries bordering the Baltic Sea. They also participate in the Baltic Assembly, a parliamentary cooperation platform, and the Nordic-Baltic Eight (NB8), a regional grouping that includes the Nordic countries and the Baltic states.
Impact of the European Union
The accession of the Baltic countries to the European Union (EU) in 2004 has had a profound impact on their economies. EU membership has provided access to the single market, facilitated trade, and attracted foreign investment. The EU’s structural and cohesion funds have also played a crucial role in supporting economic development in the region.
Regional Security
The Baltic countries, Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania, face several security challenges due to their geographical location between Russia and the West. They have been actively pursuing defense cooperation and strengthening their relationship with NATO to ensure their security.
The Baltic countries have a long history of Russian influence and occupation. After regaining independence in 1991, they sought to integrate with the West and joined NATO in 2004.
Defense Cooperation
The Baltic countries have established a strong defense cooperation framework to enhance their collective security.
- Baltic Defense College: Established in 2008, it provides military education and training to officers from the Baltic countries and partner nations.
- Baltic Air Policing: A joint air defense mission conducted by NATO forces to protect the airspace of the Baltic countries.
- Baltic Naval Squadron: A multinational naval force that conducts joint exercises and operations in the Baltic Sea.
Relationship with NATO
NATO membership is a cornerstone of the Baltic countries’ security strategy.
- Article 5 Guarantee: NATO’s collective defense clause ensures that an attack on one member state is considered an attack on all.
- Enhanced Forward Presence: NATO has deployed multinational battlegroups to Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania to deter potential aggression.
- Air Policing: NATO provides air policing support to the Baltic countries, which do not have their own fighter jets.
Environmental Issues
The Baltic Sea region faces several environmental challenges, including pollution, climate change, and habitat loss. Pollution from industrial activities, agriculture, and shipping has led to eutrophication, algal blooms, and fish kills. Climate change is causing sea levels to rise, which threatens coastal communities and infrastructure. Habitat loss due to coastal development and deforestation is reducing biodiversity and ecosystem services.
Efforts to Address Pollution and Climate Change
Efforts to address pollution and climate change in the Baltic Sea region include:
- The Helsinki Convention on the Protection of the Marine Environment of the Baltic Sea Area (HELCOM) is a regional agreement that sets environmental standards and coordinates efforts to reduce pollution and protect marine ecosystems.
- The European Union’s Baltic Sea Strategy aims to promote sustainable development and protect the marine environment of the Baltic Sea.
- National and local governments are implementing measures to reduce pollution from industrial activities, agriculture, and shipping.
- Renewable energy projects are being developed to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate climate change.
Importance of Sustainable Development
Sustainable development is essential for protecting the environment and ensuring the well-being of future generations. Sustainable development involves meeting the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. In the Baltic Sea region, sustainable development includes:
- Reducing pollution and protecting marine ecosystems.
- Mitigating climate change and adapting to its impacts.
- Promoting sustainable economic development that does not damage the environment.
- Ensuring that the benefits of development are shared equitably.
Tourism and Travel: Baltic Countries
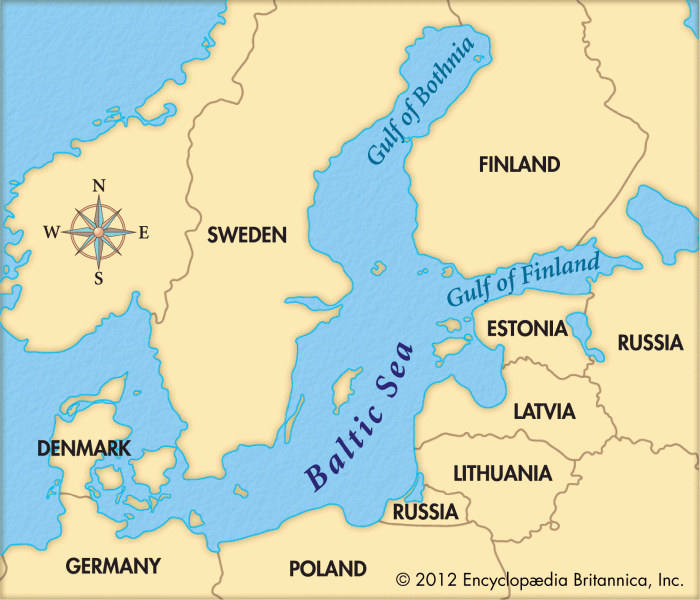
The Baltic countries offer a unique blend of history, culture, and natural beauty, making them an attractive destination for tourists. The region is home to a number of popular tourist destinations, including the medieval cities of Tallinn, Riga, and Vilnius, as well as the stunning Baltic Sea coast.
Tourism is a major industry in the Baltic countries, and the region has seen a significant increase in tourist arrivals in recent years. In 2019, the Baltic countries welcomed over 15 million tourists, and this number is expected to continue to grow in the years to come.
Popular Tourist Destinations
- Tallinn, Estonia: The capital of Estonia, Tallinn is a beautiful medieval city with a rich history. The city is home to a number of well-preserved medieval buildings, including the Toompea Castle and the Old Town Hall.
- Riga, Latvia: The capital of Latvia, Riga is a vibrant city with a rich cultural heritage. The city is home to a number of Art Nouveau buildings, as well as a number of museums and art galleries.
- Vilnius, Lithuania: The capital of Lithuania, Vilnius is a historic city with a beautiful Old Town. The city is home to a number of churches, monasteries, and other historical buildings.
- The Baltic Sea Coast: The Baltic Sea coast is a popular destination for tourists who enjoy swimming, sunbathing, and other beach activities. The region is home to a number of beautiful beaches, including the Jurmala Beach in Latvia and the Palanga Beach in Lithuania.
Tips for Planning a Trip to the Region
- When to go: The best time to visit the Baltic countries is during the summer months (June-August), when the weather is warm and sunny. However, the region can also be beautiful in the spring and fall, when the temperatures are milder.
- How to get there: The Baltic countries are easily accessible by air, land, and sea. There are a number of international airports in the region, and there are also regular train and bus services from neighboring countries.
- Where to stay: There is a wide range of accommodation options available in the Baltic countries, from budget hostels to luxury hotels. It is important to book your accommodation in advance, especially if you are traveling during the peak season.
- What to do: There are a number of things to see and do in the Baltic countries. In addition to visiting the popular tourist destinations, you can also explore the region’s natural beauty, visit its museums and art galleries, or enjoy its nightlife.
- How to get around: The Baltic countries are relatively small, and it is easy to get around by public transportation. There are regular bus and train services between the major cities, and there are also a number of rental car companies available.
Last Recap
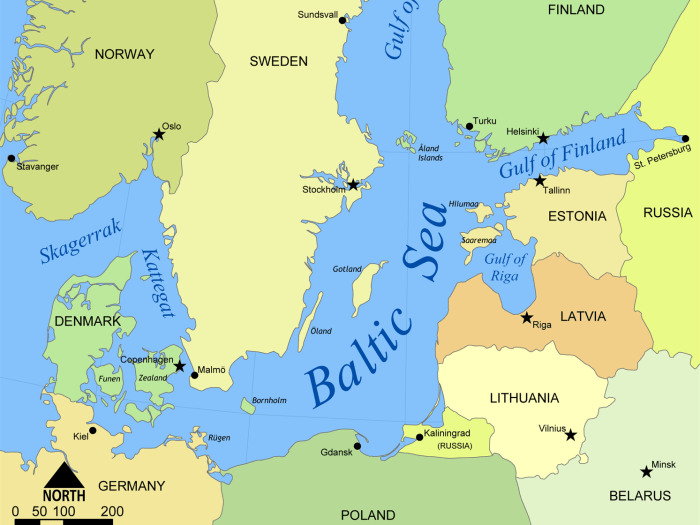
As the Baltic countries continue to navigate the challenges and opportunities of the 21st century, their resilience and determination serve as a testament to their enduring spirit. Their commitment to cooperation, both within the region and beyond, ensures that the Baltic Sea region will remain a vibrant and dynamic hub of commerce, culture, and innovation.
FAQ Overview
What are the Baltic countries?
The Baltic countries are Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania, located on the eastern coast of the Baltic Sea.
What is the history of the Baltic countries?
The Baltic countries have a rich and complex history, dating back to the Middle Ages. They have been ruled by various powers, including Denmark, Sweden, Russia, and Germany.
What are the cultural traditions of the Baltic countries?
The Baltic countries have unique cultural traditions, including folk music, dance, and art. They also have a strong tradition of storytelling and mythology.
What is the economic situation of the Baltic countries?
The Baltic countries have experienced significant economic growth in recent years. They are members of the European Union and have adopted the euro as their currency.
What are the security challenges facing the Baltic countries?
The Baltic countries face security challenges due to their proximity to Russia. They are members of NATO and have close ties with the United States.